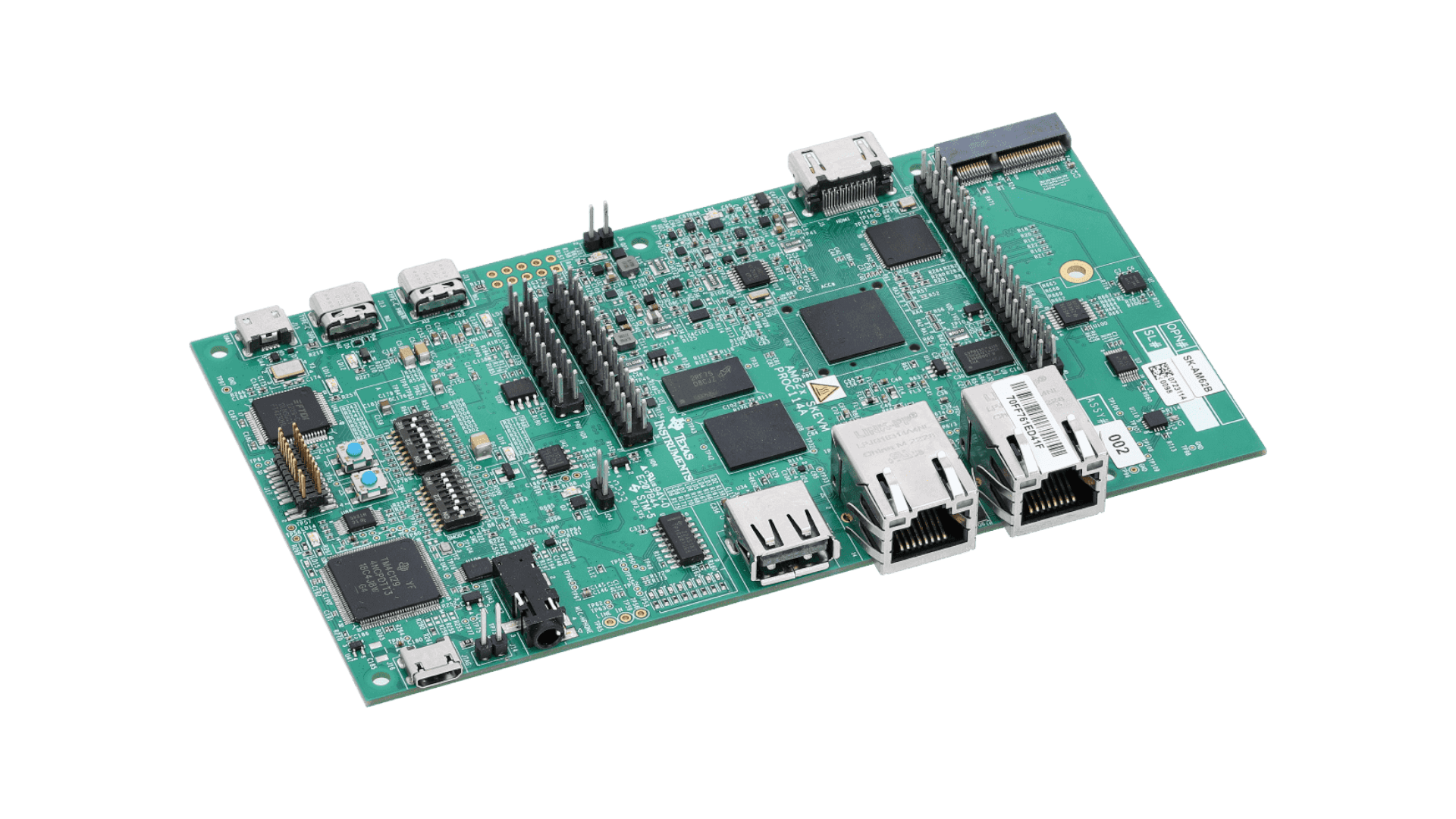
The low-power AM62x starter kit (SK) evaluation module (EVM) is a stand-alone test and development platform built around the AM62x system-on-a-chip (SoC). AM62x processors are comprised of a quad-core 64-bit Arm®-Cortex®-A53 microprocessor, single-core Arm Cortex-R5F microcontroller (MCU) and an Arm Cortex-M4F MCU.
SK-AM62-LP allows the user to experience a dual-display feature through high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) [over dots per inch (DPI)] and low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) up to 2K resolution, as well as industrial communication solutions using serial, Ethernet, USB and other interfaces. Its powerful Arm performance, up to quad-A53 at 1.4 GHz with rich interfaces, offers good control and communication capabilities for a wide range of applications, such as programmable logic controllers (PLC), automation control or a monitor/supervisor system.